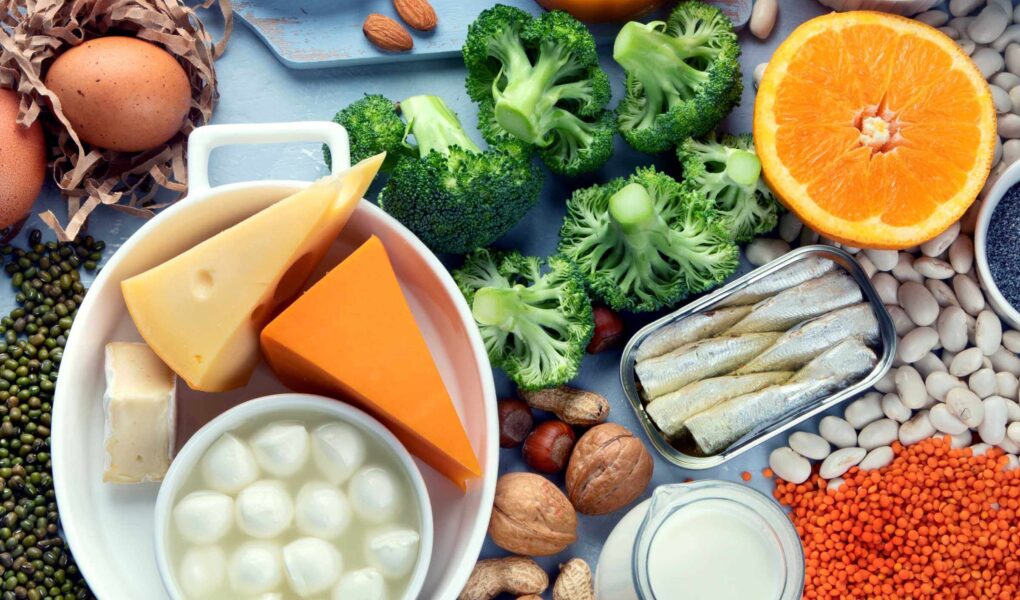
Have you ever dreamed of having luscious hair, glowing skin, and strong nails that don’t break easily? Well, the secret to achieving these beauty goals may be as simple as incorporating keratin rich foods into your diet.
In this article, we will explore the top 18 foods high in keratin to add to your grocery list that will help you achieve healthy locks, glowing skin and strong nails.
But first, you should know;
What is Keratin?
Keratin is a structural protein that is the key component of hair, nails, and skin. It’s a non-living protein, which means that it doesn’t have any metabolic functions. Instead, it acts as a building block that provides strength, elasticity, and protection to our hair and against skin damage. Also, keratin can be found in internal organs lining and glands.
As a type of protein, keratin is essential for maintaining healthy and vibrant locks. Your body naturally produces keratin, but factors like age, diet, and environmental stressors can affect the keratin synthesis process. Many people turn to keratin supplements and treatments to replenish and repair damaged keratin in their hair.
Now to the main point:
Best Keratin Rich Foods
1. Eggs

Eggs are an excellent source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, which makes them a powerhouse for hair health. They are particularly rich in biotin (vitamin B7), with a single large egg containing around 10 mcg of biotin. Biotin is crucial for keratin production, so regularly consuming eggs can significantly contribute to stronger, healthier hair, skin and nails.
2. Onions
Onions may not be the initial food choice that comes to your mind when considering hair health, however, they contain a valuable plant antioxidant known as N-acetylcysteine. This antioxidant is converted by the body into an amino acid called L-cysteine, which is a vital component of keratin (1). Furthermore, onions are abundant in folate, an essential nutrient that promotes hair growth and strengthens hair follicles. So, adding onions to your meals not only enhances flavor but also provides a beneficial boost of nutrients to support optimal hair, skin and nail health.
3. Salmon
Salmon is rich in protein, providing around 7.31 grams of protein per 1-ounce (28.4 gram) serving. It is also an exceptional source of biotin, a vital nutrient that supports keratin production. In 3 ounces (85 grams) of canned salmon, you can get 5 mcg of biotin, which is 17% of the daily value (DV) for biotin. This fish is also high in omega-3 fatty acids (healthy fat for the heart) that have been proven to enhance hair growth, and hair density, and protect against hair loss when taken as a supplement (2, 3).
4. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are a rich source of provitamin A carotenoids such as beta carotene that are converted into vitamin A in the body. Vitamin A plays a crucial role in promoting the synthesis of keratin, which is essential for maintaining healthy hair, skin and nails. In addition, sweet potatoes also provide significant amounts of vitamins B6 and C, potassium, and manganese. Just a medium-sized sweet potato weighing 150 grams can provide 1,150 mcg i.e. over 100% of the recommended daily value of provitamin A.
5. Sunflower Seeds

Sunflower seeds are an excellent snack choice that is both palatable and convenient. They are packed with essential micronutrients including copper, selenium, vitamin E, folic acid, and pantothenic acid. Plus, these seeds offer plenty of biotin and protein, which are crucial for the production of keratin. Consuming a mere 1/4 cup (35 grams) of sunflower seeds can provide you with 7 grams of protein and 2.6 mcg of biotin, amounting to 9% of the Daily Value (DV).
6. Garlic
Garlic is a great source of N-acetylcysteine, similar to an onion. According to a 2016 study, garlic also has the potential to protect keratinocytes from damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet rays. Additionally, garlic contains important beneficial micronutrients such as manganese, vitamin B6, and vitamin C.
7. Kale
Kale is one of the most nutrient-dense leafy greens, making it a powerhouse for maintaining healthy skin, nails and hair. It is an excellent source of vitamins A and C, which are essential for promoting keratin production. In just 1 raw cup of kale, you can get 50 mcg of provitamin A, which supports keratin synthesis, making up 6% of the daily value. Vitamin C, found in kale, is a water-soluble nutrient and antioxidant that stimulates collagen production, which helps maintains the skin’s strength, structure, and elasticity.
8. Beef Liver
Beef liver might not be everyone’s favorite dish, but it is incredibly rich in nutrients beneficial for you. Just 3 ounces (85 grams) of cooked beef liver can supply you with 31 mcg of biotin, i.e., 103% of the recommended daily value. Additionally, the same serving of beef liver contains a considerable amount of protein (24.5 grams) and vitamin A (7,960 mcg), which is 884% of the daily value. Beef liver is also abundant in other essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, folate, riboflavin, and iron.
9. Carrots
Carrots are an excellent source of provitamin A. A mere 1 chopped cup (128 grams) of carrots contains 1,070 mcg of provitamin A i.e., over 100% of the Daily Value. Additionally, carrots are rich in vitamin C, which promotes collagen synthesis. Furthermore, carrots are a good source of biotin, vitamin B6, potassium, and vitamin K1, which can all contribute to healthy hair growth. So, add beta-carotene-rich carrots(raw or cooked) to your meal.
Learn the Benefits of Carrots for Hair Growth!
10. Almonds

Almonds are a versatile and delicious snack that is packed with nutrients beneficial for you. This variety of nuts is rich in biotin, which is essential for keratin production, and vitamin E, which supports your overall hair strength, smooth skin and stronger nails.
11. Mangoes
Including mangoes in your diet support keratin synthesis. These tropical fruits boast a considerable amount of provitamin A, with 89 mcg per 165 grams, providing nearly 10% of the daily value. Also, mangoes are high in other crucial nutrients, such as vitamin C and folate.
12. Avocados
Avocados are a delicious fruit that offers numerous benefits for your beauty goals. They are a rich source of natural oils, i.e., polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acids. These good fats can moisturize and nourish all hair types, especially dry and dehydrated ones. Its additional vitamin content also improves the health, shine, and hydration of hair and scalp. Biotin, a B-complex vitamin, found in avocado can support hair growth, particularly in individuals with biotin deficiency. Additionally, minerals in avocado oil such as potassium and magnesium can seal cuticle cells, preventing hair breakage, and improving its smoothness and shine.
13. Blueberries
Blueberries are the richest source of antioxidants and fiber. Moreover, blueberries are high in vitamins A, C, and E, which help increase collagen stimulation and oxygenation, promoting healthy hair growth. Also, a lack of vitamin B12 in your diet may lead to premature greying of your hair. Fortunately, blueberries are rich in this essential nutrient, which can prevent this problem and provide your hair with the necessary nutrition.
14. Coconut
Coconut and coconut oil products have gained popularity for their numerous health benefits. Rich in healthy fats and essential vitamins, coconut is an excellent source of nutrients that support the formation of keratin. Using coconut oil on your hair or incorporating coconut into your diet can lead to stronger, more resilient and shiny hair.
15. Dark Chocolate

Dark chocolate is not only a delicious treat but also a fantastic dietary source of nutrients for your hair. The antioxidants in dark chocolate can help protect hair from damage, while essential minerals, such as zinc and iron, support hair growth and strength. Opt for dark varieties with a high cocoa content to get the most benefits for your hair.
16. Pumpkin Seeds
These small seeds have significant benefits for your hair. They are packed with biotin, zinc, and omega-3s, along with vitamins A, E, and K. Plus, pumpkin seeds contain linoleic and oleic acids that play a crucial role in regulating androgen levels in the body, which is one of the primary causes of hair loss. Additionally, they contain cucurbitin, an amino acid that can promote hair growth.
17. Cooked Spinach
As I mentioned earlier, green leafy vegetables are beneficial for your health. In fact, spinach can boost your hair volume. Iron deficiency is a known cause of hair loss, but just one cup of cooked spinach contains 6.5 milligrams of iron. It’s important to note that cooking spinach helps release natural iron absorption inhibitors. So, to get the most out of spinach, make sure to cook it properly.
Now, on your next shopping trip, ensure to add these keratin rich foods to your cart. You can enjoy these delicious foods, knowing that you’re not only satisfying your taste buds but also nourishing your hair.
| Food Sources of Keratin | Key Nutrients for Keratin Production |
| Eggs | Biotin, Protein |
| Onions | Quercetin, Sulfur |
| Salmon | Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Protein |
| Sweet Potatoes | Vitamin A, Beta Carotene |
| Sunflower Seeds | Vitamin E, Biotin |
| Garlic | Sulfur |
| Kale | Vitamin A, Vitamin C |
| Beef Liver | Vitamin A, Vitamin B5, Vitamin B6 |
| Carrots | Beta Carotene, Vitamin A |
| Almonds | Biotin, Vitamin E |
| Avocados | Vitamin E, Biotin |
| Blueberries | Vitamin C |
| Cinnamon | Antioxidants |
| Coconut | Healthy Fats, Vitamins |
| Dark Chocolate | Antioxidants, Zinc, Iron |
| Pumpkin Seeds | Zinc, Magnesium, Biotin |
| Cooked Spinach | Vitamin A, Iron, Folate |
Benefits of Keratin-Rich Foods
Incorporating keratin-rich foods into your diet offers many benefits including but not limited to:
Boosts Hair Growth and Density
Keratin, a structural protein, forms the building blocks of your hair, skin, and nails. By consuming keratin-rich foods, you provide your body with essential nutrients to support hair growth and density.
Enhances Hair Shine and Strength
Dull, brittle hair can be a thing of the past when you nourish your body with keratin-rich foods. By strengthening the hair shaft and improving its elasticity, these essential proteins can give your hair a healthy, shiny appearance.
Prevents Hair Loss
Hair loss can be a frustrating problem for many, but keratin can come to your rescue. A diet rich in keratin helps prevent hair loss by reinforcing the hair follicles and reducing hair breakage.
Supports Skin Health and Texture
Keratin isn’t just great for your hair, but it’s also essential for maintaining healthy skin. By maintaining skin elasticity and providing a protective barrier against environmental damage, keratin can help improve your skin texture, aid in wound healing and even provide an anti-aging effect on wrinkles and fine lines.
Promotes Nail Health
If you’re struggling with weak, brittle nails, keratin-rich foods can offer a helping hand. By strengthening the nail bed and promoting nail growth, keratin can help you achieve healthy, strong nails.
In short, a diet rich in keratin can work wonders for your hair, skin, and nails.
What Is Keratin Made Of?
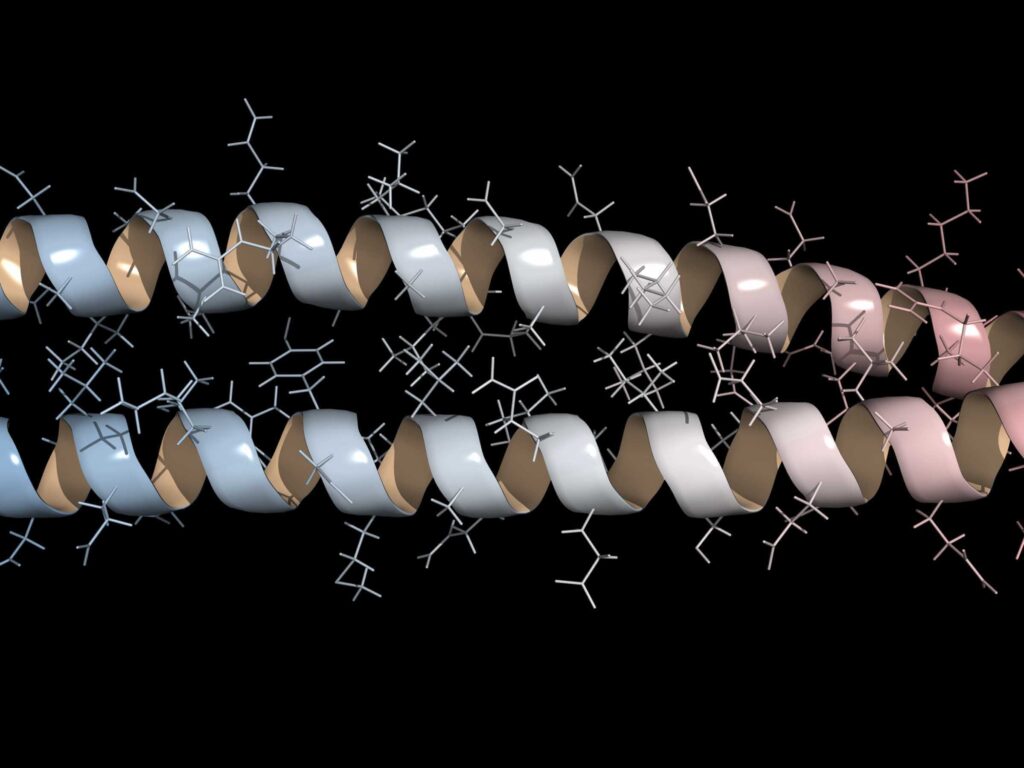
Keratin is a fibrous structural protein made up of long chains of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and in the case of keratin, they form a polypeptide chain. This chain is coiled into an alpha-helix structure, which is further stabilized by disulfide bridges.
Disulfide bridges are strong covalent bonds formed between the sulfur atoms of two cysteine amino acids within the polypeptide chain. These bridges contribute to the strength and rigidity of the keratin protein, making it resistant to external forces and degradation. The presence of disulfide bridges is one of the key factors that determine the properties and functionality of keratin in various tissues.
Keratin is a key component of hair, nails, and the outer layer of skin, as well as other structures in animals, such as hooves, feathers, and claws. It provides strength, resilience, and protection to these tissues against mechanical stress and environmental factors.
It exists in two forms: hard and soft, the two types of keratin. Hard keratin is present in hair and nails, while soft keratin is found in skin and mucous membranes. Keratinocytes, cells in the skin’s outer layer, produce keratin. As these cells mature, they migrate to the skin’s surface, eventually shedding as dust. The body continually generates new keratinocytes, a process known as cell turnover. During their journey to the surface, keratinocytes acquire keratin, which imparts their hard, protective qualities (4).
Nutrients That Help Produce Keratin
To produce keratin effectively, our body needs specific nutrients. Including foods rich in these nutrients can improve hair health and promote keratin production. So, what are these essential nutrients and their food sources?
Protein
As the building block of keratin, consuming sufficient protein is essential for healthy hair. A diet lacking in protein can lead to weakened hair, resulting in breakage and hair loss. Incorporate a variety of protein-rich foods into your diet, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Biotin
Biotin, also known as vitamin H or B7, plays a vital role in keratin production. Biotin-rich foods help maintain hair health and can even reduce hair loss in cases of biotin deficiency. Some excellent sources of biotin include eggs, almonds, spinach, sweet potatoes, and salmon.
L-cysteine
L-cysteine is an amino acid that helps form the chains of amino acids that make up keratin. This essential nutrient promotes hair growth, strength, and elasticity. Foods high in L-cysteine include poultry, egg, beef, dairy products, whole grains and legumes like lentils and chickpeas.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential micronutrient that plays a crucial role in the reproduction and development of keratinocytes. These keratinocyte cells assist in keratin production. Some fantastic sources of zinc include oysters, beef, pumpkin seeds, and whole grains.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin that aids in the production of collagen. It also helps our bodies absorb iron, an essential mineral for hair growth. Citrus fruits, such as oranges and grapefruits, are excellent sources of vitamin C, as are strawberries, kiwi, and bell peppers. Furthermore, it helps in the formation of keratinocytes essential for keratin production.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that supports hair growth by helping to regulate the production of sebum, a natural oil that moisturizes the scalp. Foods rich in vitamin A include green leafy vegetables, carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, turnip greens, and cantaloupe. Enjoy these vibrant, nutritious foods and watch your hair shine with health.
How to Increase Keratin?
Whether you’re dealing with thinning hair, brittle nails, or dull skin, there are several other simple and effective ways to boost your body’s production of keratin. Besides eating keratin-rich foods or adding keratin to your hair through keratin treatment, why don’t you give the following a try?
Consume Biotin-rich Diet
To enhance your keratin levels, consume biotin-rich foods such as eggs, nuts, seeds, nut butter, quinoa and whole grains. Additionally, you can take a biotin supplement to ensure you’re getting enough of this vital nutrient.
Include Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Your Diet
Fatty fish products like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s, while flaxseeds and walnuts also provide these essential fats.
Increase the Intake of Vitamin C
Citrus fruits, strawberries, kiwis, and bell peppers are all rich in vitamin C. By incorporating these foods into your balanced diet, you’ll provide your body with the nutrients it needs to boost keratin production.
Prioritize Cysteine in Diet
Cysteine can be found in protein-rich animal products like chicken, turkey, and dairy products. For those following a plant-based diet, soybeans, lentils, and sunflower seeds are excellent sources of cysteine. Prioritizing cysteine-rich foods in your diet can help improve your hair’s keratin levels.
Use Keratin-based Hair Products
In addition to adjusting your diet, consider using hair products that contain keratin. These products can help strengthen and protect your hair from damage, promoting a healthier appearance. However, it’s essential to use these products as recommended and not overuse them, as this could lead to protein overload.
Avoid Extreme Use of Hair Styling Products
Excessive use of hair styling products like flat irons, curling irons, electric hair straighteners and hair dryers damages keratin structure in your hair. So, to protect your hair, limit your use of these tools and try to embrace your hair’s natural texture whenever possible.
Limit Hair Bleaching
Hair bleaching can strip your hair of its natural keratin, leaving it vulnerable to damage. To maintain healthy levels of keratin, try to limit your hair bleaching or opt for gentler coloring methods instead.
Protect Hair from Sun Damage
Prolonged hair exposure to the sun can break down your hair’s keratin, leading to weakened strands. Wearing a hat or using a UV-protective hair product can help shield your hair from the sun’s harmful rays.
Rinse Hair Properly After Swimming
Chlorine and salt water can strip keratin from your hair, leaving it susceptible to damage. After swimming, be sure to rinse your hair thoroughly to remove any residual chlorine or saltwater.
Conclusion
Incorporating keratin rich foods into your diet is beneficial for maintaining healthier, stronger and more resilient hair, skin and nails. Remember, the key to smooth skin, shiny hair and strong nails lies not only in the beauty products you use but also in the foods you consume. While consuming foods high in keratine alone may not be enough to solve all of your hair and skin problems, they can certainly help support your beauty goals when combined with a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle. So, if you’re looking to enhance the appearance of your hair, skin, and nails, consider adding some of these keratin-rich foods to your diet.
References:
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6562654/
2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25573272/